 |
Journal
of Regional Section of Serbian Medical Association in Zajecar
Year 2004 Volumen 29 Number
2 |
|
|
|
|
[ Home ] [ Gore/Up ][ <<< ] [ >>> ]
|
|
|
UDK 616.133.073 |
ISSN 0350-2899, 29(2004) 2
p.80-82 |
|
| |
Original paperClinical Significance of Ultrasound Classification
Changes of Carotid Arteries
in Patients with Coronary Disease
Milan Đorić, Branko Lović, Ivan Tasić
Institut za prevenciju, lečenje i rehabilitaciju reumatičnih i
kardiovaskularnih bolesti "Niška Banja" |
|
| |
|
|
| |
Summary: Atherosclerosis like mass
non-infective disease with its progression of generalized changes
represents pathoanatomic and patophyziologic substrate for manifestation
of carotid and coronary disease. Pathoanatomic changes which evolutes in
walls of big arteries, including carotid, are caracterized with diffuse
changes of intima, hypertrophy and with forming of focal lesions-plaques.
Different forms of necrosis, thrombosis, ulcerations and hemorrhagias are
present in such atheromathosis plaques. Those complications are the main
danger for embolisation in distal parts of arteries; moreover, they make
the occlusion with consecutive clinical and neurological presentation even
worse. We carried out ultrasonographic classification of plaques in
carotid arteries in 32 patients with the detected coronary disease using
Moore method. We got the following results grouped in the following way:
A-7 patients, B-15 patients.,C-10 patients. In group A all patients were
asymptomatic, in group B 7 patients already had TIA (transitory ischemic
attack) without neurological sequels and in C group already 9 patients had
neurological injuries with residual neurological defect.
Key words: carotid disease, atherosclerotic plaque, neurological
defect Note: summary in Serbian
Napomena: sažetak na srpskom jeziku |
|
| |
|
|
| |
INTRODUCTION
Colour Doppler echosonography is the first method of choice for the
evaluation of neck blood vessels, which significantly increases
reabillity of diagnosis and decreases the number of invasive diagnostic
procedures.
During the years of clinical investigation a certain need for
examination of carotid disease has been established, as well as its
connections with coronary disease in etiological, diagnostic and
therapeutic aspect. According to the present experiences and literary
data, those two locations are strongly connected. So, we can freely say
that its material mistake is to ignore one in clear clinical
manifestation of the other especially in the presence of multiple risk
factors, which are more or less common for both localisations (1,2,3).
Cerebro vascular disease occupies a very important place in medicine and
is very important on socio-economic level. Mortality is in the third
place, right behind cardiovascular disease and neoplasms. Morbidity per
year is about 160 on 100.000 of the examined, and it exponentially grows
during the process of aging. Man got it 5 times more often than women.
Consequences of cerebrovascular insults are very serious: 71 % of the
patients after the period of 6 months have neurological sequels and only
10% fully manage to recover and come back to previous social and
professional life (4).
Anatomic changes which may cause cerebrovascular insult are in 56%
located in bulbus, 10% in vertebral arteries, 9% in truncus
brachiocephalicus and 9% in art.carotic communis (5, 6) .
According to the literary data and personal experiences as well as
during the clinical observation of our patients we noticed that the size
of atheromathosis plaques was an important factor for both diagnosis and
treatment of those patients. Therefore, we started systematically to
examine carotid arteries in patients with the detected coronary disease. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
AIM
The aim of our study was to estimate the presence, relations and
influence of the plaques on cerebrovascular events |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
MATERIAL AND METHOD
Our study group had 32 patients, all with angiographically detected
coronary disease, 20 males and 12 females, the average age 62 ± 7 years.
Colour Doppler echosonography of the main neck blood vessels on Aquson
Sequoa C256 was performed on all our patients using linear transducer of
7 Mhertz and 50 mm deep slices. We examined intraluminal atherosclerotic
changes with B mode way, defined intimo-medial thickness over 0,05cm and
plaque like focal change of intima bigger than 2mm. Intimo-medial
thickness was measured on the posterior wall of common carotid artery
and we took 3 measures during diastole. The size of the plaques was
determined by Moore's method:
- minimal arterial ulcerations or irregularities smaller
than 10mm2
- significantly bigger ulcerations area 10 to 40mm2
- big, unhomogen ulcer, area more than 40mm2
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
RESULTS
|
|
| |
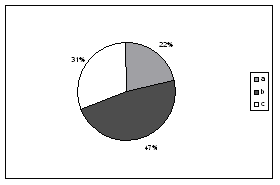 |
Among 32 examined
patients we found minimal arterial ulcerations smaller than 10mm - group A
in seven of them (22%), in 15 (48%) significantly bigger ulcerations area
10-40 mm was detected - group B whereas in 10(31%) patients big, unhomogen
ulcer was present with area more than 40 mm2 -
group C10 (figure 1). |
|
| |
Figure 1. Percentage
distribution in study group |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
In group A all our patients were subjectively and clinically
asymptomatic, which brings us to conclusion that smaller plaques doesn't
significantly impact the brain function.
In group B 7 patients already got transitor ischemic attack without
neurological defects.
In C group 9 patients had hemi paresis with residual sequels. All
changes are located on contra lateral side and their number is account
of all particularly.
Such relation shows us the dominant influence of size and type of
atheromathosis plaques on evolution of cerebrovascular disease. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
DISCUSSION
The problem of atheromathosis and stenotic lesions of carotid
arteries is clinically significant, not only like isolated carotid
disease but it is connected with some other diseases which require
medicament or surgical treatment (cardiovascular disease, strictly
controlled diabetes, big intra abdominal surgery, transplantations, even
some orthopaedic procedures) (7, 8).
It is well-known that brain of healthy, young adult has circulation of
about 800-1000ml/min.Brain consumes 15 % of volumen, 20%of calories, 20%
of blood and about 20% of oxygen consumption.
Brain flow is directly connected with pressure and resistance in blood
vessels. Further more, structural changes of vessels and changes in
blood viscosity have direct impact on cerebral perfusion although brain
is capable of auto regulating mechanisms in orderto keep perfusion on a
certain level. Changes of blood pressure, frequency and volumen have
direct influence on perfusion of other organs. This is possible due to
the permanent accommodation in small cerebral arteries, arteriolas and
capilars so, brain flow is last which is compromited in cardial and
peripheral circulatory insufficiency.
Serious compromitation of cerebral auto-regulation is present after
certain period of unregulated hypertension, prolonged hypotension and
acidosys. The loss of cerebral auto regulations is present after 20
minutes of hypoxia, and is re-established after 6-7 hours of regular
oxygenation. Brain circulation is constant and doesn't change with
changes of systemic blood pressure if its between 60-170 mmHg. Chromnic
hypertension is getting auto regulating mechanisms on higher levels.
Moor and his assistant showed a direct correlation between stenosis,
size and characteristics of plaques. Therefore, we should identified the
risk groups among asymptomatic patients which have stenosis with
degeneration of plaques, according to the previous authors. Doppler
result is 94 % of the patients sensitive to intrapalqual hemorrhagic,
while it is specific in 88%. Embolism from exulcerated plaques brings up
the transitor ischemic attack or cerebrovascular insult and if the
silent zones of brain are affected it can pass by like clinically
unrecognised.
Symptomatic ulcerogened lesion, although homodynamic insignificant is
nowadays an absolute indication of endartherectomy (8).
Our results are fully in accordance with the references and states from
literature. Therefore, such results make us very confident in our
efforts to promote this Moore method as a practical one, not only in
routine clinical praxis but in further scientific examinations of
coronary disease as well. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
CONCLUSION
- Colour Doppler echosonography of carotid arteries offers detection
and estimation of pathoanatomical and pathophysiological changes in
carotid arteries of coronary patients.
- Using Moores method of classification of severity and significance
of carotid arteries plaques is important for the evaluation of
cerebrovascular sypthomatology and proper treatment.
- This method is non-invasive, reproducible and should be a part of
diagnostic algorithm for every proved coronary patient.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
REFERENCES
- WOSCOPS (West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study): Implications
for clinical practice. Euro Heart Journal. 1996 ,17: 163-164
- Assman G.Lipid metabolism disorders and coronary heart disease ed
G.Assman, Munich.MV Medizin Verlag, 1998; 143-143
- Consensus Group, Consensus statement on the management of patients
with asymptomatic atherosclerotic carotid bifurcation lesions
,International Angiology1995, Vol 14 N0 1-.92-104
- Dawber TR.The Framingham Study. The epidemiology of
atherosclerotic disease. Cambridge: Harward Universiti press,
1980.;143-65
- Rodney A. White, Atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis, CRC,
Florida,1996.;29-33
- Born GVR, Richardson PD:Mechanical properties of human
atherosclerotic lesions. In pathology of the Human Atherosclerotic
Plaque edited by Glasgov S, Newman WP, Shaffer SA.New York; Springer
1998;68-79
- Fuster V. Syndromes of atherosclerosis .Correlation of Clinical
Imaging and pathology, American Heart Association,1996;1.;44-67
- Gross,W.S., Verta, M.J. et all . Comparation of non-invasive
diagnostic techniques in carotid artery occlusive disease, Surgery,
1997;87-271
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Corresponding Address:
Milan Đorić,
Petra Velebita 13, 18000 Niš,
tel: 018-337-083, 063-433-795
e-mail: mdjoric@EUnet.yu |
|
| |
|
|
| |
Paper received: 15. 04. 2004.
Paper accepted: 10. 06. 2004
Published online: 05. 08. 2004. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[ Home ] [ Gore/Up ][ <<< ] [ >>> ]
|
|
|
Infotrend Crea(c)tive Design |
|
|
|
Revised:
20 May 2009
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

